Quantum Computing: Unlocking the Future of AI Innovation and Sustainability
Quantum computing represents a transformative leap in computational technology, harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics to tackle problems beyond the reach of classical computers. As we navigate the challenges of advancing artificial intelligence (AI) and achieving sustainability, quantum computing emerges as a potential game-changer. This article explores how quantum computing can meet the computational demands of AI innovation while contributing to the global green transition, supported by specific examples and insights from leading research.
 Grok
GrokQuantum Computing and AI: A Powerful Synergy
AI, particularly in its advanced forms like large language models (LLMs) and complex neural networks, requires immense computational resources. Training these models can take weeks or months on classical supercomputers, consuming vast amounts of energy. Quantum computing offers a promising solution by leveraging quantum bits (qubits), which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to superposition and entanglement. This enables quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical systems, making them ideal for AI applications involving optimization, machine learning, and big data processing.
Key Benefits for AI
- Faster Model Training: Quantum machine learning algorithms could significantly reduce the time required to train AI models, enabling the development of more sophisticated and accurate systems. For instance, Quantinuum highlights that quantum computers can address the computational bottlenecks of classical LLMs, which are expensive and error-prone.
- Enhanced Data Processing: Quantum computing can process vast datasets more efficiently, improving AI’s ability to analyze complex information, as noted in Capitol Technology University.
- Quantum Neural Networks: Research from Scientific American suggests that quantum transformers could mimic brain-like functions, potentially leading to more efficient and capable AI systems.
- Optimization and Simulation: Quantum computing excels at solving optimization problems and simulating complex systems, which are critical for AI applications in fields like drug discovery and financial modeling, according to InformationWeek.
These advancements could take AI to new heights, enabling innovations that are currently limited by classical computing constraints. However, as Polytechnique Insights cautions, quantum computing and AI may not be as compatible as hoped due to current technological limitations, suggesting a need for cautious optimism.
Sustainability Benefits: Quantum Computing for a Greener Future
Beyond enhancing AI, quantum computing holds significant promise for advancing sustainability across various industries. By solving complex problems that classical computers struggle with, quantum computing can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices, aligning with global goals like the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (Pasqal).
Specific Applications for Sustainability
McKinsey & Company estimates that quantum computing could reduce CO2 emissions by over 7 gigatons by 2035 through applications like:
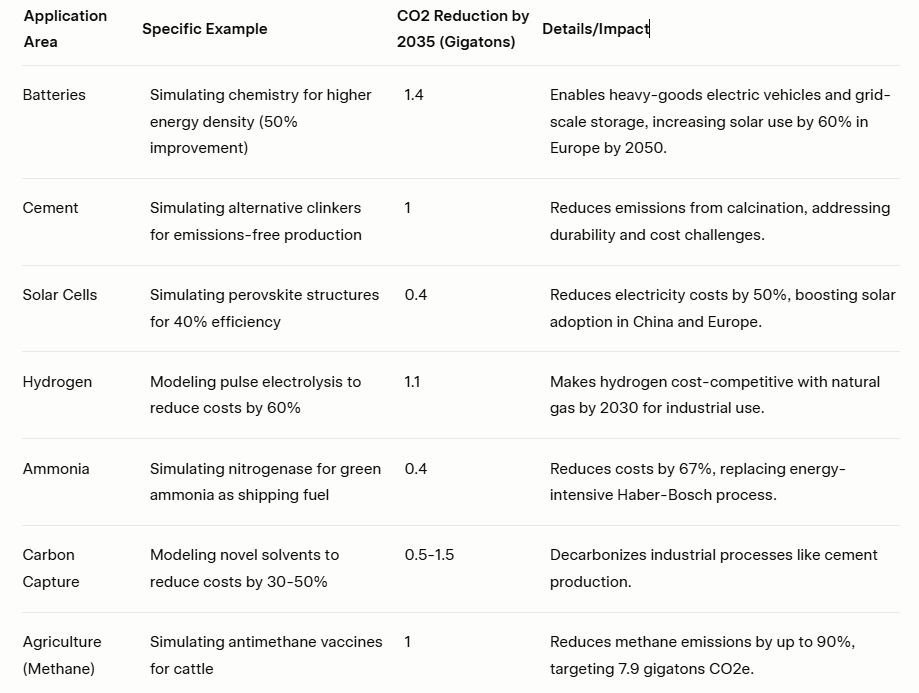 Source: Table was created by the author.
Source: Table was created by the author.These applications demonstrate quantum computing’s potential to address persistent sustainability challenges by optimizing processes, discovering new materials, and improving energy efficiency. For example, IBM Research emphasizes its role in sustainable chip manufacturing and carbon capture, while Quantum Zeitgeist highlights its ability to optimize logistics and supply chains, reducing energy consumption.
Making AI More Sustainable
AI’s energy consumption is a growing concern, with training a single natural language processing model producing over 626,000 pounds of CO2 — nearly five times the lifetime emissions of an average American car (TechUK). Quantum computing’s efficiency in performing computations could significantly reduce the energy required for AI operations, lowering its carbon footprint. By speeding up tasks like model training and optimization, quantum computing could make AI development more environmentally friendly, as suggested by Zapata AI.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, quantum computing faces environmental challenges that must be addressed to ensure its sustainability benefits. Many quantum systems, particularly those using superconducting qubits, require extreme cooling to near absolute zero, consuming significant energy. TechUK notes that this cooling can make quantum computers more energy-intensive than classical systems in some cases.
However, innovative solutions are emerging:
- Room-Temperature Quantum Computing: Platforms like ORCA Computing use single photons for qubits, operating at room temperature without cryogenic cooling.
- Trapped Ion Systems: These can function without ultra-low temperatures, reducing energy demands.
- Sustainable Frameworks: Research, such as the Carbon-aware Quantum Computing framework, aims to calculate the carbon footprint of quantum platforms, promoting responsible development.
EY emphasizes the duality of technology, noting that quantum computing both augments and challenges sustainability goals. Continued research is essential to balance these factors and maximize environmental benefits.
Conclusion
Quantum computing stands at the intersection of AI innovation and sustainability, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. By enhancing AI’s computational capabilities, it can drive breakthroughs in fields like drug discovery and financial modeling. Simultaneously, its ability to optimize energy systems, develop sustainable materials, and reduce emissions positions it as a key player in the green transition. To fully realize these benefits, the research community must address the environmental challenges of quantum computing itself, such as energy-intensive cooling. By developing sustainable quantum technologies and frameworks, we can ensure that this revolutionary technology not only powers the future of AI but also contributes to a healthier planet.
Key References
- Quantum computing just might save the planet
- Could Quantum Computing hold the key to sustainability?
- Quantum Computers Will Make AI Better
- Quantum Computers Can Run Powerful AI That Works like the Brain
- Quantum computing and AI: less compatible than expected?
- Enabling Quantum Computing with AI
- Quantum Computing and AI: A Perfect Match?
- The Relationship Between AI and Quantum Computing
- Supercharging AI with Quantum Computing: A Look into the Future
- Quantum AI: Explaining how it will impact the business world
- If You Think AI Is Hot, Wait Until It Meets Quantum Computing
- Three ways quantum computers may benefit society
- Quantum Computing for Sustainability: A Practical Guide
- Sustainable Quantum Computing: Opportunities and Challenges
- How Quantum Computing Can Tackle Climate and Energy Challenges
- How quantum supports sustainability
- Quantum Computing and AI to Enable Our Sustainable Future
- Quantum Computing And The Environment: How It Can Aid Sustainability
- How can your quantum vision be transformed into a sustainable reality
Quantum Computing: Unlocking the Future of AI Innovation and Sustainability was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
