Top 20 AI Crypto Coins Set to Lead the Market in 2025
Stablecoins have the potential to significantly drive the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications by providing much-needed stability in an otherwise volatile crypto market. As DeFi relies on digital assets for lending, borrowing, trading, and staking, the inherent price fluctuations of cryptocurrencies can pose risks to users and developers alike. Stablecoins, by maintaining a fixed value typically pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar, offer a reliable alternative that reduces these risks.

This stability encourages broader adoption of DeFi platforms, as users are more confident in their investments and transactions. Furthermore, stablecoins enhance liquidity within DeFi ecosystems, allowing for seamless interactions between different platforms and use cases. By bridging the gap between traditional financial systems and decentralized networks, stablecoin development also contribute to the overall growth of the DeFi space, making it more accessible, scalable, and secure. As the demand for more stable, reliable, and transparent financial solutions increases, stablecoins are poised to play a pivotal role in the future of decentralized finance.
Table of ContentWhat is Stablecoin Development?The Role of Stablecoins in DeFi
Advantages of Stablecoins for DeFi Ecosystem
How Stablecoins Can Strengthen the DeFi Ecosystem?
Choosing the Right Blockchain for Stablecoin Development
Use Cases of Stablecoins in DeFi
Challenges and Risks of Stablecoins in DeFi
Future Outlook: Stablecoins and the Future of DeFi
ConclusionWhat is Stablecoin Development?
Stablecoin development refers to the process of creating digital currencies that are pegged to a stable asset, such as a fiat currency (e.g., USD) or a commodity (e.g., gold), to minimize price volatility and offer a reliable store of value. The development of stablecoins involves designing and implementing smart contracts, algorithms, or collateralized assets to ensure that the coin’s value remains stable over time. There are three primary types of stablecoins: fiat-backed, crypto-backed, and algorithmic.
Fiat-backed stablecoins are directly pegged to a reserve of a fiat currency, while crypto-backed stablecoins use other cryptocurrencies as collateral. Algorithmic stablecoins rely on supply and demand mechanisms controlled by algorithms to maintain price stability. The process includes rigorous testing and validation to ensure the stability, security, and scalability of the coin, often utilizing blockchain technology to provide transparency and decentralization.
Stablecoin development aims to create digital currencies that are not only useful for day-to-day transactions but also provide liquidity and reduce risks in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, making them a crucial component of the blockchain ecosystem.
Join @CoinCodeCap on TelegramThe Role of Stablecoins in DeFiStablecoins play a critical role in the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem by bridging the gap between traditional fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies. They are digital assets designed to maintain a stable value, typically by being pegged to a fiat currency like the U.S. dollar or assets such as gold. Their stable value makes them ideal for use in decentralized applications (dApps) and financial services, which traditionally rely on the volatility of cryptocurrencies.
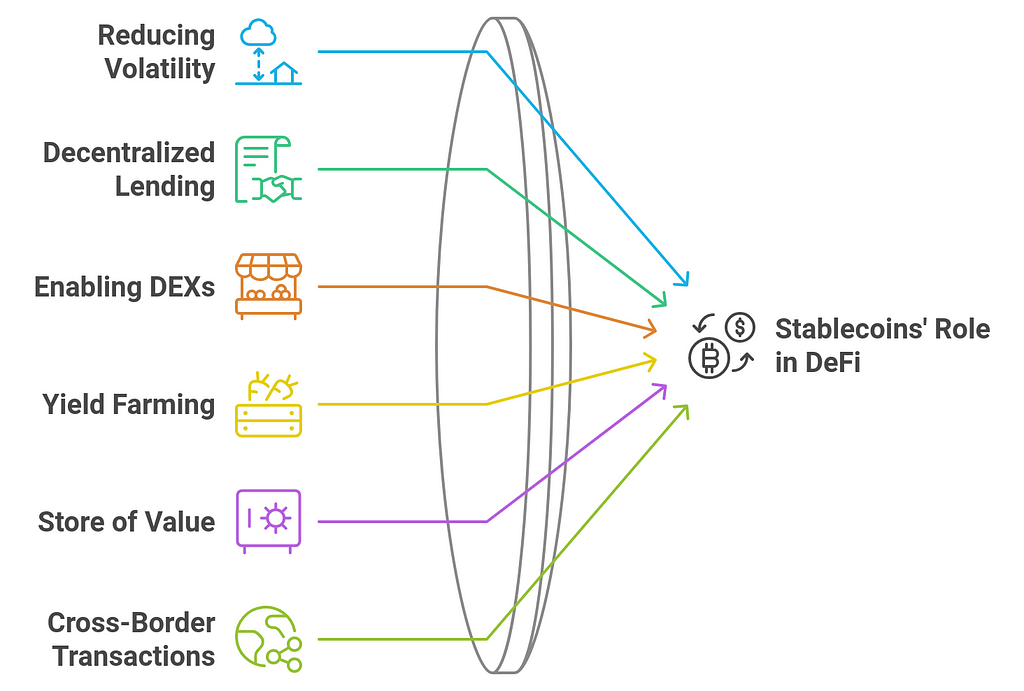
Here’s a detailed look at the role of stablecoins in DeFi:
1. Reducing Volatility- Problem: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, while valuable and widely used, are highly volatile. This volatility can deter users from using them for everyday transactions or as collateral in financial applications, as the value of the asset can change dramatically within short periods.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins solve this problem by offering price stability. They maintain a value of 1:1 with a fiat currency (like USD) or other pegged assets. This stability makes them a reliable medium of exchange in DeFi platforms, where users need to transact or collateralize assets without worrying about large fluctuations in value.
- Example: USD Coin (USDC), Tether (USDT), and DAI are popular stablecoins that peg their value to the U.S. dollar, providing a stable currency for transactions within DeFi protocols.
- Problem: In traditional lending and borrowing markets, loans are typically denominated in fiat currencies. The volatility of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, makes it difficult to use them as collateral for lending or borrowing on decentralized platforms.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins allow for loans to be denominated in a stable asset, ensuring that the value of both the collateral and the loan remains consistent. This enables decentralized lending platforms to operate efficiently, as both borrowers and lenders can avoid the risks associated with crypto volatility.
- Example: In platforms like Compound or Aave, users can deposit stablecoins like DAI, USDC, or USDT as collateral to borrow other assets or earn interest on their deposits.
- Problem: Cryptocurrency exchanges often have low liquidity, especially for smaller or less popular assets. This issue is exacerbated by the volatility of cryptocurrencies, making it hard for users to trade without facing significant price slippage.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins provide liquidity on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), as they are widely accepted and stable in value. They act as a trading pair on DEXs, allowing users to exchange stablecoins for other cryptocurrencies or use them as a medium for transaction fees or liquidity pools.
- Example: On Uniswap and SushiSwap, stablecoins like USDC and DAI are frequently used in liquidity pools. Users can swap stablecoins for other assets without worrying about price volatility.
- Problem: In DeFi, users often seek to earn passive income through yield farming or staking. However, using volatile cryptocurrencies as the underlying asset in these processes can lead to unpredictable returns.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins enable more predictable and stable yields for users participating in yield farming or staking. By using stablecoins, users can earn interest without exposure to the risks of price fluctuations, providing a stable return on their investment.
- Example: On Yearn.finance, users can provide liquidity in stablecoins and earn yields through automated strategies, allowing them to earn passive income in a more stable manner compared to volatile crypto assets.
- Problem: Cryptocurrencies, though highly valuable, are not always suitable as a stable store of value due to their price volatility. This creates challenges for users who want to protect their wealth in a decentralized ecosystem without holding traditional fiat currencies.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins serve as a store of value within the DeFi ecosystem. Users can convert their volatile crypto holdings into stablecoins when they want to protect their value from market swings while remaining within the DeFi space.
- Example: A user might convert volatile Bitcoin or Ethereum into DAI or USDT to safeguard their portfolio from a market downturn while still having access to DeFi protocols.
- Problem: Traditional cross-border payments can be slow, expensive, and cumbersome, especially for people in regions with limited access to banking services or those facing currency devaluation.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins make cross-border payments fast, inexpensive, and decentralized. Since they are stable and widely accepted, users can send stablecoins across borders with low fees and immediate settlement times, without the need for intermediaries.
- Example: A user in the U.S. could send USDC or DAI to a recipient in another country in seconds, bypassing traditional financial institutions, exchange rates, and associated fees.
- Problem: Traditional financial systems often require personal information to conduct transactions, posing a privacy risk for users. Additionally, cryptocurrency transactions on public blockchains are often visible, which can compromise user privacy.
- Stablecoin Role: Many stablecoins, especially those built on privacy-focused blockchains, offer enhanced privacy features. In DeFi, users can transact using stablecoins while maintaining some level of anonymity, particularly if they use privacy-enhancing technologies or privacy coins integrated with stablecoin systems.
- Example: Some stablecoins built on the Zcash blockchain or integrated with privacy solutions like Monero might offer enhanced privacy features, making them appealing for users who prioritize financial privacy.
- Problem: Traditional assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate are often illiquid and require intermediaries. Moreover, governance in traditional finance typically involves centralized entities, leaving little room for decentralized decision-making.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins can serve as tokenized representations of real-world assets, such as property or commodities. In DeFi, stablecoins can be used for voting and governance purposes, allowing decentralized organizations or DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) to make decisions based on stable assets.
- Example: A DAO could use stablecoins like DAI as a governance token to vote on proposals or to collateralize real-world assets within tokenized protocols.
- Problem: In traditional finance, there are complex risk management tools, such as insurance and hedging, to manage risk exposure. In DeFi, the lack of stability in crypto assets makes risk management more challenging.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins enable more predictable risk management strategies within DeFi protocols, such as decentralized insurance, where users can pool funds in stablecoins to insure other users against smart contract risks, market crashes, or other DeFi protocol failures.
- Example: Protocols like Nexus Mutual provide decentralized insurance products in which participants can stake stablecoins and insure others against smart contract failures, providing a form of risk mitigation.
- Problem: Many institutions remain cautious about participating in DeFi due to concerns about volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
- Stablecoin Role: Stablecoins offer a regulated and predictable asset class within the DeFi space. Institutions can participate in DeFi without exposing themselves to significant market volatility, fostering increased adoption of DeFi by institutional investors and financial entities.
- Example: Institutions can use USDC or DAI to participate in yield farming, staking, and liquidity provision without worrying about wild fluctuations in the value of their holdings.
Stablecoins play a vital role in the DeFi ecosystem by providing stability, liquidity, and accessibility in a space traditionally known for its volatility. They enable a range of financial services in decentralized environments, from lending and borrowing to yield farming, staking, and cross-border payments. By addressing volatility concerns, stablecoins bring traditional financial assets into the blockchain space, making DeFi more user-friendly and suitable for both retail and institutional investors. As the DeFi space grows, the role of stablecoins will continue to expand, helping to create a more accessible, efficient, and scalable decentralized financial ecosystem.
Advantages of Stablecoins for DeFi EcosystemStablecoins offer several advantages that make them essential to the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem. They provide stability, reduce volatility, and enhance the overall user experience in decentralized applications (dApps). Here are some key advantages of stablecoins for the DeFi ecosystem:
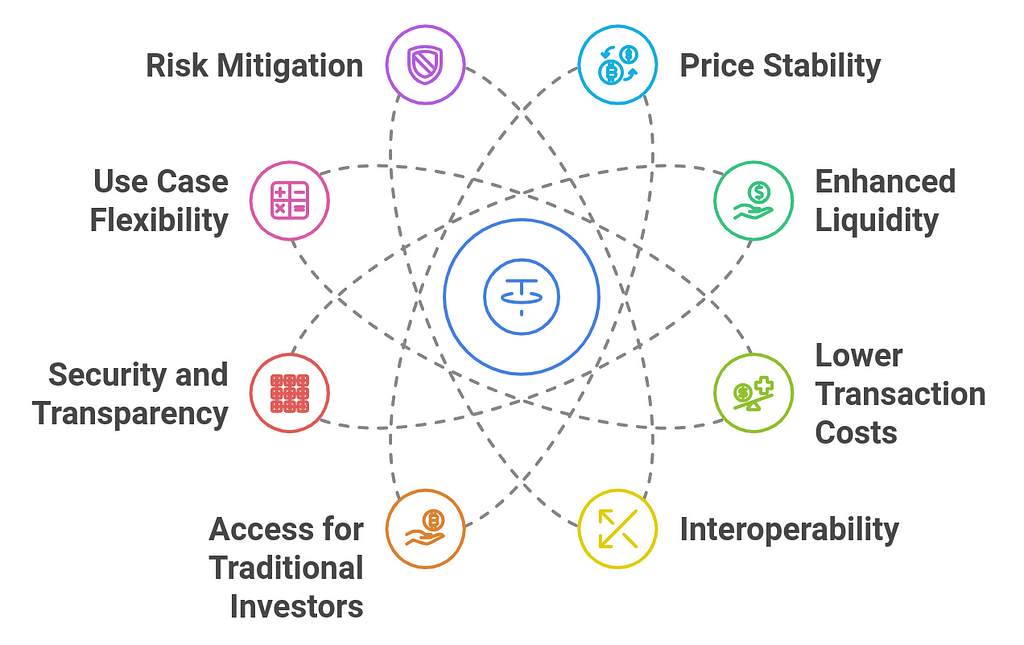 1. Price Stability
1. Price Stability- Advantage: Stablecoins are designed to maintain a consistent value, often pegged to a fiat currency like the U.S. dollar or other assets like gold. This stability makes them an ideal choice for use in DeFi applications that require predictable, stable pricing.
- Impact: DeFi platforms and users can avoid the large price fluctuations typically associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. This stability is crucial for activities like lending, borrowing, yield farming, and liquidity provision, where volatility could lead to losses or risk of liquidation.
- Advantage: Stablecoins act as a reliable medium of exchange and store of value, attracting liquidity providers to DeFi protocols. Their widespread use ensures that there is enough liquidity in decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and other DeFi services.
- Impact: With stablecoins, liquidity providers can participate in trading, lending, or staking activities without worrying about the volatility of their assets. This liquidity helps drive better pricing, more trades, and a smoother DeFi experience.
- Advantage: Compared to traditional finance, stablecoin transactions often have lower fees, especially in DeFi ecosystems that run on public blockchains like Ethereum, Polygon, or Binance Smart Chain.
- Impact: Stablecoins facilitate low-cost and fast transactions, which is particularly useful for microtransactions, cross-border payments, and frequent trading, making them attractive for users who would otherwise face high fees with traditional financial systems.
- Advantage: Stablecoins provide an interoperable solution across multiple DeFi platforms and blockchains. Most major DeFi platforms accept stablecoins like DAI, USDC, and USDT, allowing seamless movement of funds between protocols and blockchain ecosystems.
- Impact: This interoperability enables users to diversify their investments, participate in cross-chain DeFi protocols, and access a broader range of financial services without worrying about currency compatibility or conversion rates.
- Advantage: Stablecoins bridge the gap between traditional fiat-based finance and the rapidly growing world of DeFi. Their stability makes them a less risky entry point for traditional investors who may be hesitant to participate in the volatile world of cryptocurrencies.
- Impact: By using stablecoins, investors can enter the DeFi ecosystem with a lower risk profile, giving them access to innovative DeFi products like lending, borrowing, and yield farming, while still having their funds denominated in a stable asset.
- Advantage: Stablecoins built on blockchain technology offer a high level of transparency and security. All transactions are recorded on an immutable blockchain, allowing users to track the movement of funds and ensuring that the supply of stablecoins is properly collateralized and auditable.
- Impact: This level of transparency builds trust within the DeFi ecosystem, as users can be confident that their funds are secure, and the underlying assets backing the stablecoins are verifiable. Additionally, transparency reduces the risk of manipulation or fraud.
- Advantage: Stablecoins are versatile and can be used across various DeFi use cases, including lending, borrowing, yield farming, liquidity pools, derivatives, and more.
- Impact: The broad utility of stablecoins makes them an integral part of many DeFi protocols. They can be used for collateralization, earning passive income, staking, and even in decentralized insurance protocols, driving the expansion of DeFi and its accessibility.
- Advantage: By using stablecoins, DeFi users can mitigate the risks associated with the extreme volatility of cryptocurrencies. For example, during market downturns, users can move their funds into stablecoins to preserve value while avoiding potential losses from price swings.
- Impact: This flexibility allows users to protect their portfolios, ensuring that they are not exposed to excessive risk in highly volatile markets. Additionally, stablecoins act as a hedge for DeFi platforms offering fixed returns or lending services.
- Advantage: Stablecoins are a decentralized alternative to traditional fiat currencies. They enable access to financial services without the need for intermediaries like banks, making them particularly valuable for people in unbanked or underbanked regions.
- Impact: By facilitating decentralized financial services, stablecoins empower individuals globally to access financial tools, engage in cross-border payments, and protect their wealth, especially in areas where traditional banking infrastructure is limited or unstable.
- Advantage: Many stablecoins are designed to comply with regulatory standards, making them more appealing to institutional investors and traditional financial systems. Stablecoins like USDC are often fully backed by fiat reserves and undergo regular audits, offering additional assurance of their stability and compliance.
- Impact: As regulations around cryptocurrency and DeFi evolve, stablecoins that adhere to regulatory guidelines will likely face fewer legal challenges and continue to be a central component of the growing DeFi ecosystem, particularly for institutional adoption.
- Advantage: Many stablecoins are audit-ready and fully transparent about their backing assets and reserve holdings. This transparency can be seen through on-chain reports and third-party audits, ensuring that each stablecoin is backed by real, verifiable assets.
- Impact: Users and investors can have confidence in the stability of the system, knowing that their stablecoins are fully backed by reserves, which reduces the risk of a “run on the bank” scenario and helps build trust in the system.
- Advantage: Stablecoins facilitate seamless cross-border transactions. Unlike traditional cross-border transfers, which can involve high fees and delays due to currency conversions and intermediary banks, stablecoins offer a faster and more affordable alternative.
- Impact: Stablecoins can be sent and received instantly, reducing the barriers to international trade and remittances, especially for people in countries with unstable local currencies or underdeveloped financial infrastructure.
The advantages of stablecoins make them a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem, offering stability, security, and flexibility to users. They reduce volatility, attract liquidity, and provide a means for traditional investors to participate in decentralized finance. With their ability to streamline payments, facilitate lending, and empower users with decentralized financial tools, stablecoins are set to play an even more significant role in the future development of the DeFi space. As the ecosystem grows, stablecoins will continue to provide the stability and accessibility needed to support the expansion and adoption of DeFi applications globally.
How Stablecoins Can Strengthen the DeFi Ecosystem?Stablecoins are a crucial element in strengthening the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem. Their ability to maintain a stable value while offering the benefits of digital assets makes them a key building block for enabling diverse financial services without the need for traditional intermediaries. Here’s how stablecoins can strengthen the DeFi ecosystem:
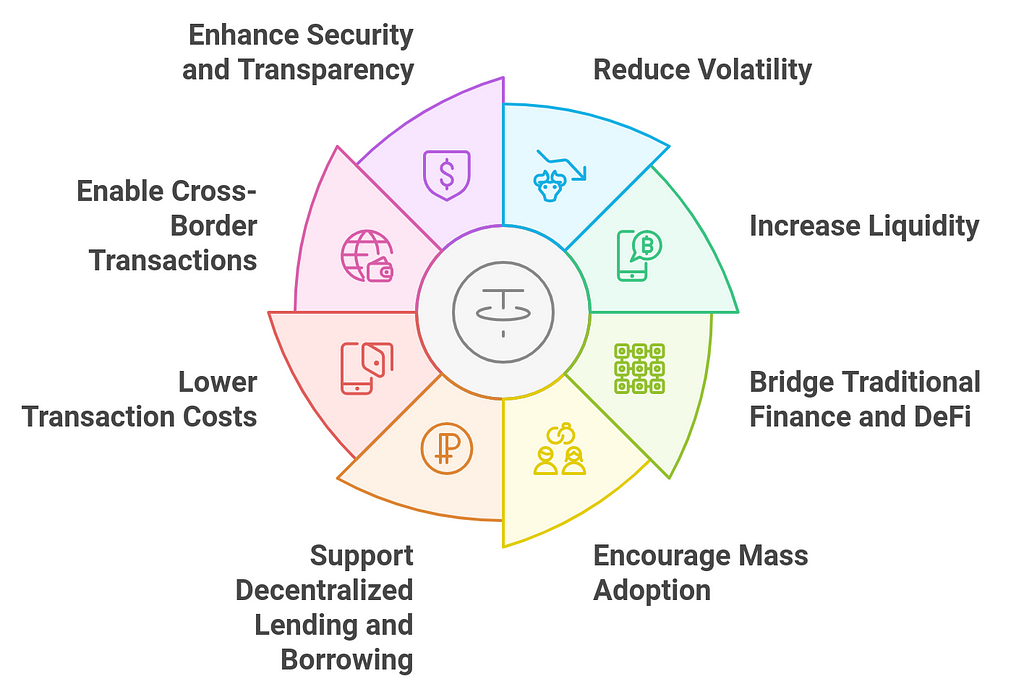 1. Reduce Volatility in DeFi Markets
1. Reduce Volatility in DeFi Markets- How It Helps: The primary advantage of stablecoins is their ability to provide price stability. In the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, users can hedge against wild price swings by converting their assets into stablecoins. This stability is crucial in DeFi platforms where users are involved in lending, borrowing, and liquidity provision.
- Impact: Stablecoins reduce the risk of liquidation and impermanent loss, making them ideal for DeFi applications. By allowing users to lock in stable value, stablecoins enhance the security and reliability of decentralized platforms, encouraging broader participation.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins are widely used as a medium of exchange and a store of value. They play a key role in providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending protocols, and yield farming platforms.
- Impact: With their stable nature, stablecoins attract liquidity providers who want to participate in DeFi without exposure to the volatility of other cryptocurrencies. This liquidity enables smoother operations in DeFi applications, making them more efficient and scalable.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins act as a bridge between the traditional financial system (fiat currencies) and the DeFi ecosystem. By being pegged to traditional currencies like the USD, EUR, or GBP, they allow users from traditional finance to interact with DeFi protocols without the need to exchange their fiat for volatile cryptocurrencies.
- Impact: This interoperability helps bring institutional capital and more traditional investors into DeFi, as they are more likely to engage with stablecoins than volatile crypto assets. The seamless transfer of funds between traditional and decentralized finance promotes growth and expansion within the DeFi ecosystem.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins lower the barrier to entry for new users, especially those who are wary of the volatility of other cryptocurrencies. By offering a stable asset that operates within the decentralized ecosystem, stablecoins make DeFi more accessible to the average person or institution.
- Impact: As stablecoins become more widely accepted and understood, they encourage a wider range of participants including users from regions with volatile local currencies or unstable financial systems to adopt DeFi services. This expanded user base can contribute to the network effects, driving the overall growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins are widely used as collateral for decentralized lending and borrowing platforms. Their stability makes them less risky as collateral, reducing the chances of borrowers facing liquidation due to market volatility.
- Impact: In DeFi lending protocols such as Aave, Compound, or MakerDAO, stablecoins allow users to earn interest on deposits or borrow funds at fixed or variable rates. This provides an alternative to traditional finance, enabling users to access credit without intermediaries, all while keeping the value of their assets stable.
- How It Helps: Using stablecoins for transactions within DeFi platforms can lower the costs associated with exchanging volatile cryptocurrencies. Many DeFi applications enable fee-less or low-cost stablecoin transactions, making microtransactions and cross-border payments more efficient.
- Impact: By reducing the cost of transactions, stablecoins make decentralized applications more user-friendly and accessible. This is especially important for micropayments, remittances, and everyday use cases that require quick, low-cost transactions.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins enable instant, low-cost, and borderless transactions, making them an ideal solution for cross-border payments and remittances. People in different parts of the world can send and receive funds in stablecoins without the delays or high fees associated with traditional banking and remittance services.
- Impact: This fosters financial inclusion, especially for people in unbanked or underbanked regions. The accessibility and ease of using stablecoins for international transactions drive the broader adoption of decentralized finance globally, helping to connect users to a larger financial ecosystem.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins, like other blockchain-based assets, benefit from the inherent transparency and security of blockchain technology. Transactions involving stablecoins are recorded on public blockchains, allowing users to track their assets and ensuring that the stablecoins remain fully collateralized.
- Impact: This transparency reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation and builds trust in DeFi platforms. For example, USDC and DAI undergo regular audits and report their reserve holdings, providing a sense of security for users and encouraging participation in DeFi activities.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins can be used as collateral in derivative markets or for creating synthetic assets (assets that mirror real-world assets, like stocks, commodities, or indices). By using stablecoins, users can maintain a stable value while engaging in sophisticated financial products.
- Impact: This expands the range of DeFi products available, making it easier for users to engage in asset diversification, speculation, and hedging strategies. Stablecoins are crucial for enabling the creation of decentralized synthetic assets that track traditional markets, providing DeFi users with exposure to broader financial markets.
- How It Helps: Since many stablecoins are fully collateralized and comply with regulatory standards, they offer a level of transparency and accountability that other cryptocurrencies may lack. This makes stablecoins more attractive to regulators, institutions, and traditional finance players.
- Impact: As stablecoins gain more regulatory approval, they will likely become more widely adopted in both traditional and decentralized finance systems. This regulatory clarity promotes institutional adoption and enhances the legitimacy of the DeFi ecosystem, attracting more users and investors to the space.
- How It Helps: Stablecoins make micropayments more feasible, as they can be sent with low fees, regardless of the amount. This enables creators and service providers to monetize their content by receiving small payments for access, tips, or rewards.
- Impact: For platforms that rely on micropayments, such as content creators, game developers, or streaming services, stablecoins provide a way to monetize their work without incurring high fees. This increases the flow of small transactions and makes the DeFi ecosystem more active and diverse.
Stablecoins are integral to the success and expansion of the DeFi ecosystem. They offer essential benefits like price stability, increased liquidity, reduced volatility, and accessibility for both users and institutions. By providing a stable store of value, stablecoins support decentralized lending, borrowing, liquidity provision, and trading, while enabling efficient cross-border payments and reducing friction in decentralized applications. As the DeFi space continues to grow, stablecoins will remain a key driver of innovation, adoption, and broader financial inclusion in decentralized finance.
Choosing the Right Blockchain for Stablecoin DevelopmentChoosing the right blockchain for stablecoin development is a crucial decision that directly impacts the performance, security, scalability, and adoption of the stablecoin. The blockchain chosen will affect the technical architecture, transaction costs, and the overall ecosystem in which the stablecoin will operate. Here’s a guide to help navigate the key considerations when selecting a blockchain for stablecoin development:
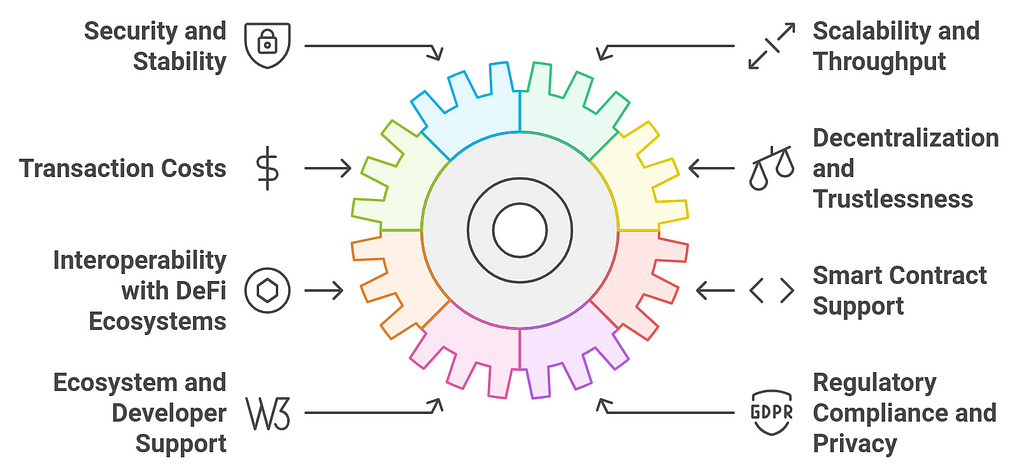 1. Security and Stability
1. Security and Stability- Why It Matters: A stablecoin’s security is critical, as users entrust it with value. The blockchain hosting the stablecoin must be secure and resistant to attacks such as double-spending, 51% attacks, and other vulnerabilities.
- What to Look For: Blockchains with a proven track record of network security and resilience, like Ethereum, Bitcoin (via the Lightning Network), and Solana, are good options. Ensure that the blockchain uses strong consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS), that maintain network integrity.
- Why It Matters: As stablecoin adoption grows, the blockchain must be capable of handling a high volume of transactions efficiently. This is particularly important if the stablecoin is used in high-frequency trading, remittances, or other applications requiring fast transactions.
- What to Look For: Opt for blockchains that can scale effectively, such as Ethereum 2.0 (with Proof-of-Stake), Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and Solana. These networks are designed to handle large transaction volumes while maintaining performance.
- Why It Matters: Transaction fees are a significant factor in user adoption. If transaction costs are too high, especially for small transactions, it could hinder the stablecoin’s utility in DeFi applications and daily use.
- What to Look For: Blockchains like Binance Smart Chain and Polygon offer significantly lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum (especially before Ethereum’s scaling solutions like Layer-2 rollups become widely adopted). Lower fees encourage mass adoption, particularly in DeFi.
- Why It Matters: A core feature of stablecoins and DeFi is the trustless and decentralized nature of the underlying blockchain. The blockchain should not have central points of failure, which could undermine the decentralized nature of the stablecoin.
- What to Look For: Choose a decentralized blockchain like Ethereum or Bitcoin, which has a large number of independent validators. This ensures that no single entity has control over the network, thus reinforcing trust in the stablecoin’s stability and decentralization.
- Why It Matters: Stablecoins are often used within the broader DeFi ecosystem. The blockchain selected must be compatible with popular DeFi platforms and applications, enabling seamless integration for lending, borrowing, yield farming, and trading.
- What to Look For: Ethereum is the most established blockchain for DeFi, but other chains like Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, and Fantom are also compatible with popular DeFi protocols. Interoperability with decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and liquidity pools is crucial for driving adoption.
- Why It Matters: Most stablecoin projects are powered by smart contracts that automate functions like minting, redeeming, and collateral management. The blockchain should support robust smart contract functionality.
- What to Look For: Ethereum is the leader in smart contract functionality, but other blockchains such as Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, and Cardano offer powerful smart contract capabilities. Evaluate the blockchain’s support for programming languages (e.g., Solidity on Ethereum, Rust on Solana) and developer tools.
- Why It Matters: A blockchain with a large and active developer community will provide better support for building and maintaining the stablecoin project. Strong community engagement leads to faster development and continuous improvements.
- What to Look For: Ethereum has the largest developer ecosystem for DeFi and smart contracts, but blockchains like Solana and Polkadot are quickly growing in popularity. Look for a blockchain with good documentation, developer resources, and an established community to ensure a smooth development process.
- Why It Matters: As the regulatory landscape around stablecoins continues to evolve, it’s crucial to choose a blockchain that is compatible with both compliance requirements and privacy standards.
- What to Look For: Layer-2 solutions or sidechains (e.g., Polygon, Optimism) can offer privacy features like zk-rollups for privacy-preserving transactions. If regulatory concerns around stablecoins arise, it is also essential to ensure the blockchain’s ability to support features like compliance monitoring and AML/KYC requirements.
- Why It Matters: Governance mechanisms on the blockchain determine how the network evolves, how decisions are made, and how protocol upgrades are implemented. The governance structure can impact the stability and reliability of a stablecoin project.
- What to Look For: Look for decentralized governance (e.g., DAO structures) that allows stakeholders to participate in decision-making. Blockchains like Ethereum and Polkadot have strong governance features that enable token holders to vote on important protocol changes.
- Why It Matters: The ultimate success of a stablecoin depends on the adoption of the blockchain it’s built on. A blockchain with an established user base and strong network effects will help the stablecoin gain traction more quickly.
- What to Look For: Blockchains with established user bases such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana are ideal for stablecoins. Additionally, evaluate the blockchain’s adoption rate in key sectors such as DeFi, gaming, and NFTs, as these can provide an early user base for the stablecoin.
When choosing a blockchain for stablecoin development, the decision depends on your project’s technical requirements, market focus, and long-term goals. Ethereum remains a strong contender due to its maturity and established ecosystem, but Solana, Polygon, and Binance Smart Chain also offer compelling benefits, especially in terms of transaction costs and scalability. Regulatory concerns, privacy features, and developer support should also play a key role in the decision-making process.
Use Cases of Stablecoins in DeFiStablecoins have become essential in the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem due to their ability to maintain price stability while providing liquidity and efficiency. Here are several key use cases of stablecoins in DeFi:
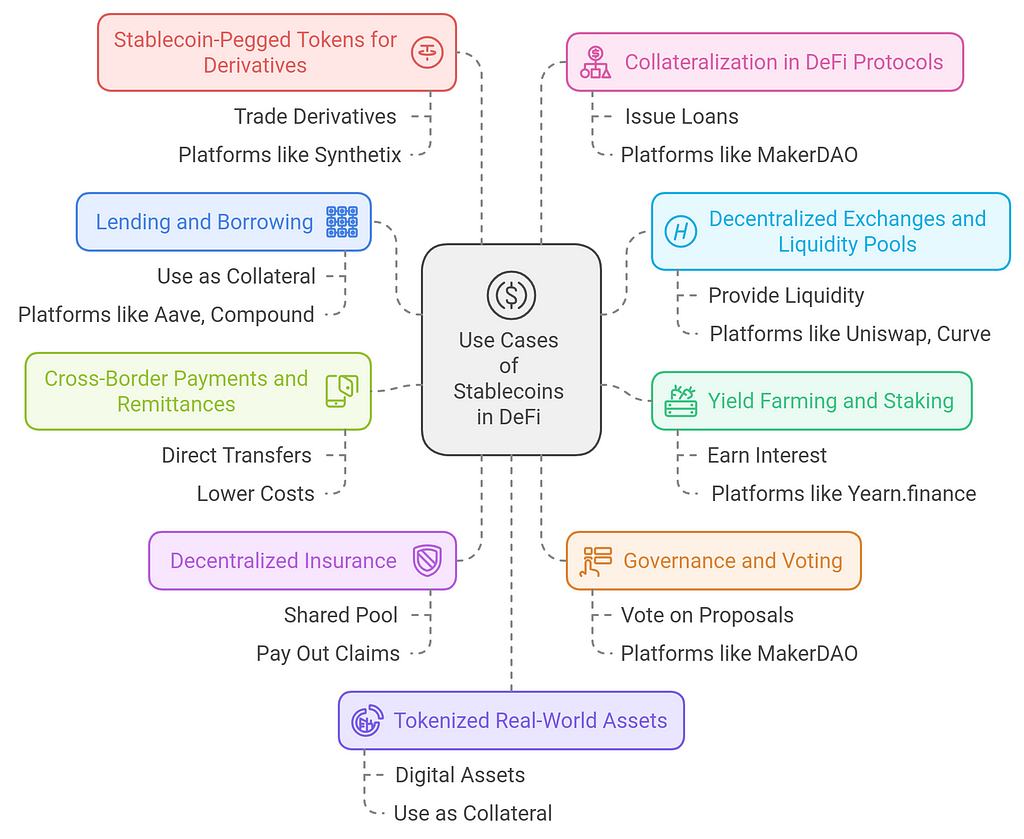 1. Lending and Borrowing
1. Lending and Borrowing- Use Case: Stablecoins are widely used as collateral in decentralized lending and borrowing platforms. Since stablecoins are pegged to fiat currencies like the U.S. dollar, they are less volatile than other cryptocurrencies, making them ideal for collateralizing loans.
- How It Works: In platforms like Aave, Compound, or MakerDAO, users can deposit stablecoins like DAI, USDC, or USDT into liquidity pools and earn interest. Borrowers can take out loans against their stablecoin deposits or other crypto assets with low volatility, avoiding the risk of liquidation due to market swings.
- Example: A user deposits USDC as collateral and borrows DAI to invest in other DeFi protocols, all while keeping the value of their collateral stable.
- Use Case: Stablecoins are commonly used on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and in liquidity pools due to their stability, which attracts liquidity providers. Their stable value reduces the risk of slippage and impermanent loss in trades.
- How It Works: On platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap, or Curve Finance, users provide liquidity by depositing stablecoins into liquidity pools. In return, they earn a share of the transaction fees generated on the platform.
- Example: A liquidity provider deposits USDT and USDC into a stablecoin pool on Curve Finance and earns transaction fees from users swapping stablecoins.
- Use Case: Stablecoins offer an attractive option for yield farming and staking, providing consistent returns with reduced exposure to volatile market movements. Users can stake stablecoins to earn interest, liquidity rewards, or governance tokens.
- How It Works: Yield farming protocols like Yearn.finance or Venus Protocol enable users to deposit stablecoins into farming pools or staking contracts to earn passive income. The stable nature of these coins ensures that the principal remains intact while users benefit from the platform’s rewards.
- Example: A user deposits DAI in a Yearn.finance vault to earn yield from automated strategies that invest the stablecoins in the most profitable DeFi opportunities.
- Use Case: Stablecoins enable fast, low-cost, and borderless transactions, which are especially useful for cross-border payments and remittances. Their stable value ensures that the recipient receives a predictable amount, even when transferring between countries with different currencies.
- How It Works: Instead of relying on traditional remittance services, users can send stablecoins directly to recipients worldwide. The transaction occurs instantly, with minimal fees and without the need for intermediaries or currency exchange.
- Example: A person in the U.S. sends USDC to a family member in India, who can then convert it to the local currency at a lower cost and faster speed compared to traditional banks.
- Use Case: Stablecoins are used in decentralized insurance platforms to offer coverage and payouts in a stable currency, ensuring predictable payouts to policyholders in case of claims.
- How It Works: In decentralized insurance protocols like Nexus Mutual, users contribute stablecoins to a shared pool. When claims arise (e.g., a smart contract failure or loss of funds), the stablecoins in the pool are used to pay out the claims to policyholders.
- Example: A DeFi user buys insurance coverage for their assets in a smart contract platform, and if the smart contract is hacked or fails, they are compensated with DAI or USDC from the insurance pool.
- Use Case: Stablecoins are often used in governance models for decentralized organizations (DAOs), allowing token holders to vote on proposals and decisions regarding protocol upgrades, fund allocation, and other operational aspects.
- How It Works: In governance systems like MakerDAO or Compound Governance, stablecoins can be used to participate in decision-making processes. The stable value of the coins ensures that governance tokens represent a consistent amount of economic power.
- Example: In MakerDAO, DAI holders participate in governance decisions, voting on matters such as collateral types, risk parameters, and the protocol’s overall direction.
- Use Case: Stablecoins are increasingly used as collateral for derivatives or tokenized representations of real-world assets like commodities, equities, and real estate.
- How It Works: Derivative platforms allow users to trade products that derive their value from underlying assets, such as commodities or indices. Stablecoins are used for trading these derivatives because they maintain a consistent value and can easily be integrated into smart contracts.
- Example: Synthetix, a decentralized synthetic asset platform, allows users to trade assets like synths (synthetic assets) that represent real-world assets (e.g., gold, stocks) by using DAI or USDT as collateral.
- Use Case: Stablecoins are commonly used as collateral in DeFi protocols for generating loans, leveraging assets, or issuing synthetic assets. Their stable value reduces the risk of liquidation due to price fluctuations.
- How It Works: In platforms like MakerDAO or Aave, users deposit stablecoins as collateral to issue loans in other assets (e.g., stablecoins or crypto) or participate in leveraged positions without the risk of excessive liquidation due to volatility.
- Example: A user deposits USDC as collateral to borrow DAI or other assets in a decentralized lending protocol.
- Use Case: Stablecoins can be used to tokenize real-world assets such as real estate, commodities, or traditional securities in DeFi platforms. This enables users to access these assets in a digital, decentralized manner.
- How It Works: Stablecoins can represent fractional ownership of real-world assets (RWAs) through tokenized forms. These tokenized assets can be traded, sold, or used as collateral in DeFi platforms, while maintaining a stable value.
- Example: A user can tokenize real estate into digital assets backed by DAI or USDC and use them as collateral for a loan on a DeFi platform.
- Use Case: Stablecoins facilitate micropayments in DeFi applications, enabling small transactions for goods and services, such as content streaming, gaming, or tipping.
- How It Works: Users can send stablecoins in small amounts without worrying about high transaction fees, making it ideal for content creators or services that require microtransactions.
- Example: A content creator could receive USDT or DAI as micropayments from viewers who want to access premium content, tip, or support their work.
Stablecoins provide essential functionality across many areas of DeFi. Their stable value makes them ideal for lending, borrowing, trading, and collateralization, while reducing volatility and increasing confidence in DeFi systems. They enable cross-border transactions, governance, insurance, and innovative financial products like yield farming and synthetic assets, making them a key building block in the growth and scalability of the decentralized financial ecosystem. As DeFi continues to evolve, stablecoins will likely play an even larger role in ensuring stability, liquidity, and accessibility within decentralized finance.
Challenges and Risks of Stablecoins in DeFiWhile stablecoins offer significant advantages in the DeFi ecosystem, they also face several challenges and risks. One key concern is the potential for instability in the collateralization model, particularly with algorithmic stablecoins, which can experience value fluctuations if the underlying mechanisms fail. Fiat-backed stablecoins rely on centralized reserves, creating counterparty risks and regulatory challenges, as they must comply with government regulations that vary across jurisdictions.
Additionally, over-collateralization in crypto-backed stablecoins can lead to inefficiencies and liquidity concerns. Another risk is the possibility of smart contract vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors to manipulate or steal funds. Furthermore, the growing scrutiny from regulators worldwide poses uncertainties for the future of stablecoins, as governments explore ways to introduce stricter oversight.
Finally, market volatility and shifts in investor sentiment can create situations where even stablecoins might deviate from their peg, undermining the trust and stability they aim to provide within the DeFi ecosystem.
Future Outlook: Stablecoins and the Future of DeFiThe future of stablecoins and their role in the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem looks promising, as they continue to bridge the gap between traditional finance and decentralized technologies. As the DeFi space grows, stablecoins will play a central role in driving innovation, increasing accessibility, and enhancing the stability of decentralized finance platforms. Here’s a future outlook on how stablecoins will evolve and shape the future of DeFi:
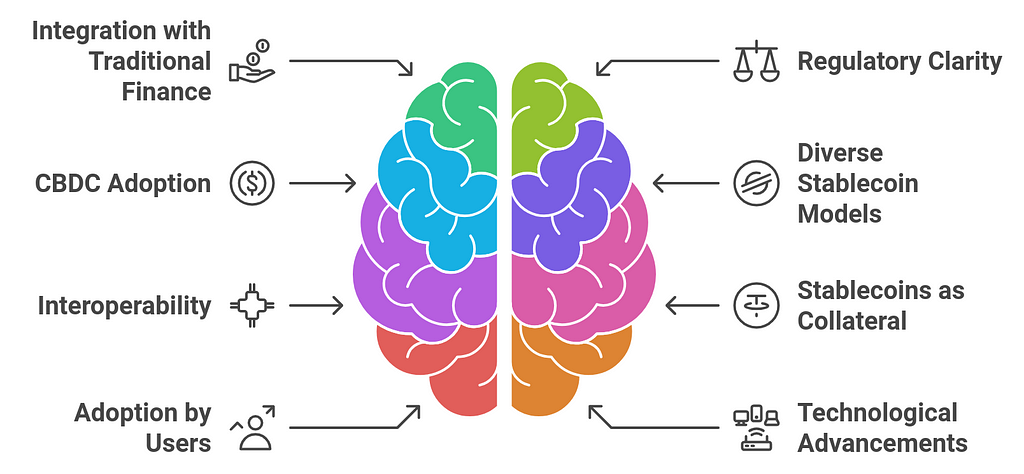 1. Increased Integration with Traditional Finance
1. Increased Integration with Traditional Finance- Outlook: As the regulatory environment around stablecoins and cryptocurrencies becomes clearer, we can expect more collaboration between DeFi platforms and traditional financial institutions. Central Banks and regulators may push for more stablecoin issuance, especially in digital central bank currencies (CBDCs), which could further legitimize stablecoins within the traditional finance system.
- Impact: This integration will result in more institutional involvement in DeFi, where traditional financial institutions may utilize stablecoins for cross-border payments, lending, and other financial services. It could also lead to the mainstream adoption of DeFi products by banks and institutional investors, bridging the gap between the old financial system and the new decentralized economy.
- Outlook: The future of stablecoins in DeFi is heavily influenced by regulatory frameworks. In the coming years, we can expect more regulatory clarity surrounding stablecoins, as governments worldwide work to establish rules for their issuance and use.
- Impact: With clearer regulations, stablecoins will likely become more widely accepted, reducing the uncertainty and risks associated with their use in DeFi. As regulations evolve, we may see more regulated stablecoins entering the market, further driving institutional adoption. Stablecoin projects that comply with local regulations could become the standard for DeFi, leading to more trust in the ecosystem.
- Outlook: Governments around the world are exploring the issuance of CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies). These digital currencies could be seen as a state-backed, regulated form of stablecoin and may coexist with or even integrate into the broader DeFi ecosystem.
- Impact: If CBDCs are adopted, they could provide more stability and confidence to DeFi users, who would benefit from a fully regulated, government-backed stablecoin. Moreover, CBDCs could facilitate faster, cheaper, and more transparent cross-border payments. The integration of CBDCs into DeFi protocols could significantly expand the use cases for decentralized finance and foster increased collaboration between public and private sectors.
- Outlook: As the DeFi space matures, we may see the development of more diverse stablecoin models beyond traditional fiat-collateralized stablecoins like USDC or Tether (USDT). For example, there is growing interest in algorithmic stablecoins and crypto-collateralized stablecoins that do not rely on fiat reserves.
- Impact: The introduction of new stablecoin models could provide greater decentralization, reduce the risks associated with centralization in the stablecoin market, and offer innovative mechanisms for stabilizing the coin’s value. The competition among different models could also lead to better products for DeFi users, with more flexibility and options for use in decentralized applications.
- Outlook: Interoperability is crucial for the future of DeFi, as it enables seamless asset transfer and interaction across multiple blockchains. The development of cross-chain protocols and bridges that allow stablecoins to move freely between blockchains could become more advanced and widespread.
- Impact: By enhancing interoperability, stablecoins can play a critical role in a more connected and efficient DeFi ecosystem. This would enable users to leverage stablecoins across different DeFi platforms, from Ethereum to Binance Smart Chain to Polkadot and Solana, ensuring greater liquidity, better pricing, and more diverse DeFi applications.
- Outlook: In the future, stablecoins will likely become even more essential as collateral in DeFi lending and borrowing protocols. As more DeFi projects integrate stablecoins into their platforms, the amount of collateralized assets tied to stablecoins will likely increase.
- Impact: This will create a more secure environment for borrowers, as they can borrow against a stable asset rather than volatile cryptocurrencies, reducing liquidation risks. As lending protocols grow, stablecoins could provide a more predictable and stable foundation for DeFi lending markets, leading to better risk management and lower interest rates for users.
- Outlook: The accessibility and price stability of stablecoins make them an attractive option for both retail and institutional investors. With growing trust in stablecoin-backed DeFi platforms, these digital assets will attract a broader audience, including retail investors, corporations, and institutions.
- Impact: More users in the DeFi ecosystem will likely drive demand for stablecoins, enabling larger pools of liquidity and better capital efficiency. As stablecoins become more trusted, they will serve as the primary medium of exchange for DeFi applications, leading to their increased use in various sectors such as insurance, gaming, and asset tokenization.
- Outlook: The technology behind stablecoins is likely to evolve, focusing on improving scalability, reducing transaction fees, and enhancing security. We can expect the development of more robust and secure smart contracts to ensure that stablecoins remain fully collateralized and their value is maintained.
- Impact: Improved technology will make stablecoins more efficient and cost-effective, which will further increase their utility in DeFi applications. As smart contracts and decentralized oracles become more sophisticated, stablecoins will continue to strengthen their role in providing security, scalability, and decentralization in DeFi protocols.
- Outlook: Stablecoins could play a crucial role in the tokenization of real-world assets (RWAs), including real estate, art, and commodities. Tokenized RWAs could be traded and accessed through DeFi platforms, where stablecoins act as a stable medium of exchange and collateral.
- Impact: Tokenizing RWAs on DeFi platforms and using stablecoins for transactions would unlock new investment opportunities, provide liquidity to traditionally illiquid assets, and increase financial inclusivity. This could lead to the democratization of asset ownership, allowing anyone with access to DeFi platforms to invest in real-world assets.
- Outlook: As the DeFi space matures, there will likely be a stronger emphasis on privacy and security. Stablecoins, being a key asset in DeFi, will need to evolve to ensure that user data and transaction privacy are protected while maintaining transparency on the blockchain.
- Impact: Privacy-focused stablecoins and enhanced privacy features (like zk-SNARKs or privacy-preserving technology) could emerge to safeguard user data while ensuring that the DeFi ecosystem remains transparent and auditable. This would build greater trust and attract privacy-conscious users, further accelerating DeFi’s mainstream adoption.
The future of stablecoins in DeFi is bright, with many promising developments ahead. As the space grows, stablecoins will play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between traditional finance and decentralized financial services, offering stability, liquidity, and new investment opportunities. The increased adoption of stablecoins by retail, institutional investors, and even governments will further solidify their importance. With advancements in technology, regulation, and interoperability, stablecoins are poised to be a core component of the decentralized economy, driving innovation and growth in DeFi for years to come.
ConclusionIn conclusion, stablecoins are essential for the continued growth and stability of the DeFi ecosystem. By providing a stable store of value, they mitigate the volatility typically associated with cryptocurrencies, making DeFi applications more accessible and appealing to a broader audience. Stablecoins enhance liquidity, allowing users to engage in activities like lending, borrowing, and trading with reduced risk and greater confidence. Their role in bridging traditional finance with decentralized networks not only strengthens the infrastructure of DeFi but also fosters trust among users and investors.
As decentralized finance continues to evolve, the demand for reliable, transparent, and efficient financial solutions will only grow, positioning stablecoins as a foundational element in shaping the future of DeFi. Their ability to offer stability, security, and scalability will continue to drive innovation, unlocking new possibilities and helping DeFi realize its full potential. Ultimately, stablecoins are set to play a critical role in reinforcing the DeFi ecosystem and ensuring its long-term sustainability.
How Can Stablecoins Drive the Growth of DeFi Applications and Strengthen the Ecosystem? was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
